Git and GitHub are powerful tools for improving your development workflow. But while they’re often mentioned interchangeably, the reality is that Git and GitHub have very different roles.
Here, we’ll break down what sets them apart, explore how they work together, and why they both have an important role to play.
What is Git?
Git is a Version Control System (VCS) that helps you track changes to your code over time. It’s free and open-source, so you can use it at no cost and even contribute to its development.
Features of Git
Git makes managing your code and working as a team easier with features like:
1. Tracks every change
With Git, every modification to your code is recorded. Anytime a bug or other issue appears, you can rewind to a previous version and see exactly what changed.
2. Encourages safe experimentation
If you ever want to test a new feature but don’t want to mess up the main project, Git lets you create different branches (separate workspaces) where you can experiment freely.
Once you’re happy with the changes, you can merge them back into the main codebase without disrupting ongoing work.
3. Supports offline work
Unlike cloud-based tools, Git operates locally on your machine. This means you can keep using it even without an internet connection. Any changes you make will sync once you’re back online.
4. Simplifies collaboration
Multiple team members can work on the same Git project at the same time without overwriting each other’s work. And when used with platforms like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket, Git becomes a powerhouse for managing inputs from teams across the globe.
5. Improves code quality
Teams in separate locations can review each other’s code before it’s merged into the main project. The result? Higher quality code, far fewer errors, easier debugging, and more stable software releases.
What is GitHub?
GitHub is a cloud-based platform (built on top of Git) that lets you store, manage, and collaborate on code repositories. It’s essentially a central hub to share projects, work together, and track changes in real-time.
Key features of GitHub
Here’s how GitHub keeps management and collaboration running smoothly:
1. Repository hosting
GitHub stores your Git repositories in the cloud, so you can access them from anywhere—anytime. This makes it simple for teams to collaborate on the same project without complicated setups.
2. Collaboration tools
With features like pull requests, issue tracking, and discussions, GitHub makes it easy for teams to manage code changes, track bugs, and communicate—all in one place.
3. Integrations
GitHub works with tools like CI/CD pipelines and project management apps to help automate tasks and keep everything running as it should.
4. Open-source community
As the home to millions of open-source projects, GitHub offers the opportunity to contribute to (or learn from) projects around the world.
5. Free and paid plans
GitHub offers a generous free plan, perfect for individuals or small teams. For more storage and advanced tools like Codespaces, you can always upgrade to a paid plan.
6. Marketplace
From testing to deployment, GitHub’s Marketplace has tons of third-party tools to improve your development workflow.
Git vs GitHub: A quick overview
| Feature | Git | GitHub |
| Definition | Version control system | Cloud-based Git repository hosting service |
| Usage | Manages code locally | Facilitates collaboration and remote access |
| Installation | Installed on your computer | Accessed via a web browser or app |
| Core functionality | Tracks code changes | Hosts repositories and provides collaboration tools |
| Offline access | Fully functional offline | Requires internet for repository access |
When to use Git vs when to use GitHub
Not sure when to use Git or GitHub? Here’s a quick guide:
- Git: Use Git when you need to manage versions of your code locally, especially if you’re working alone or don’t have internet access.
- GitHub: Use GitHub to collaborate with others, manage your projects online, and share your code with the community.
How Git and GitHub work together
Now that we understand the difference between Git and GitHub, let’s look at how you can use them together:
- Local development with Git: Write and update the code on your computer, and Git will track any changes or different versions.
- Push to GitHub: When you’re ready, push your changes to a GitHub repository so they’re accessible to others.
- Collaborate on GitHub: Your team can review your code, discuss issues, and merge changes directly on GitHub.
- Pull updates: To stay in sync with the team, pull the latest changes from GitHub to update your local code.
Common Git commands (and what they mean)
Not sure where to start? Here are some basic Git commands you can use immediately:
Basics commands
git init: Creates a new Git repository in your current foldergit clone [url]: Makes a copy of an existing repository from a remote URLgit status: Shows the current status of your files and what’s ready to be committedgit add [file/folder]: Prepares files or folders for the next commitgit commit -m "message": Saves your changes with a message describing what you’ve done
Branching and merging
git branch: Lists all the branches in your repositorygit branch [branch-name]: Creates a new branchgit checkout [branch-name]: Switches to the specified branchgit merge [branch-name]: Merges the specified branch into your current branch
Remote repositories
git remote add [name] [url]: Adds a new remote repositorygit fetch: Fetches changes from a remote repository without merging themgit pull: Fetches and merges changes from a remote repositorygit push: Pushes your local changes to a remote repository
Undoing changes
git reset [file]: Unstages a file but keeps your changes.git checkout -- [file]: Reverts changes in your working directory back to the last committed stategit revert [commit-id]: Reverts a specific commit by creating a new commit that undoes the changes
Viewing history
git log: Shows the full commit historygit log --oneline: Displays a condensed version of the commit historygit diff: Compares the changes between your working directory and the staging area
Are Git and GitHub data automatically backed up?
No, Git and GitHub don’t automatically back up your data. They operate under The Shared Responsibility Model, where Git handles the version control of your code locally on your machine, and GitHub stores and hosts your repositories in the cloud.
But it’s your responsibility to manage and protect your data. To ensure the safety of your code and avoid losing important work, it’s essential to set up your own backup process or use third-party backup tools.
Key takeaway
Git and GitHub are excellent tools for developers. Git lets you track and manage your code’s history, while GitHub makes it easy to work with others and share your projects.
They each play a role in keeping your workflow and your team on the same page. Remember, it’s important to back up your data to prevent losing your hard work.
Protect your data with BackupLABS
BackupLABS offers automated backups every 24 hours, keeping your Git and GitHub data safe.
The simple dashboard lets you track your backups in real-time, and your data is encrypted for added security. If something goes wrong, you can easily restore your data or roll back to previous versions.
Start your 14-day free trial with BackupLABS today.
Your Guide to Recovering a Deleted GitHub RepositoryOh no! Did you just accidentally delete that crucial GitHub repository? Try not to panic just yet.
While the initial shock might feel like you’ve lost years of work, there’s a good chance you can recover your lost repository. You just have to know the right steps to follow.
This guide will walk you through restoring a deleted GitHub repository and share some tips to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Why delete GitHub repositories?
Sometimes, developers hit the delete button on GitHub repositories just to keep their workspace tidy. For example, a project might start as two separate repositories but later get combined into one. When that happens, you don’t need both repos anymore, and there’s not much sense keeping the extra one lying around now, is there?
Deleting old repositories can also help avoid confusion. Outdated projects might mislead collaborators or recruiters into thinking they’re active when they’re not. Plus, it’s a great way to reduce security risks—those old repos could contain outdated dependencies or sensitive information you don’t want to leave exposed.
Why would you need to recover a GitHub repository?
Unfortunately, there are times when deleting a GitHub repository isn’t ideal. For instance, you might accidentally delete the wrong repository or delete the right one only to realise, “Oh no, I actually still need that!”
Accidental deletions might be the most common reason for needing to restore a deleted repo, but they’re far from the only one. Malicious actions by employees are another common risk. For example, if you tick off an employee or have to let someone go, they might delete an important repository out of spite. And let’s not forget the possibility of hackers gaining access to your GitHub and altering or deleting code.
You might even revisit an old project you thought you’d never need again—because priorities and circumstances can change quickly. Whatever the reason, if you’ve deleted a GitHub repository and need to get it back, it helps to know if—and how—you can do that.
What is the GitHub data retention policy?
GitHub offers a 90-day grace period for accidental deletions. During these 3 months, you can restore the repository anytime you need. So, if you’ve accidentally deleted a GitHub repo, take a breath, you may still be able to get it back.
But what happens after 90 days? The repository and all its contents are permanently deleted. And unless you’ve set up a GitHub backup solution beforehand, they can’t be recovered.
Guide to restoring GitHub
There are 2 primary methods for restoring your valuable GitHub data. These are:
Method 1: Restore GitHub using GitHub Cloud
To restore a deleted repository using GitHub Cloud, take the following steps. But don’t forget: Only repositories deleted within the last 90 days are recoverable via GitHub Cloud.
- Log in to GitHub: Use the account where the repository was created initially and ensure you have the appropriate permissions
- Go to your repositories: Click your profile picture in the upper-right corner and select Your Repositories. For organisation-owned repositories, visit the organisation’s page first
- Find deleted repositories: Scroll to the bottom of the repositories list. If any repositories can be restored, they’ll appear in a Deleted Repositories section
- Restore the repository: Locate the repository you want to restore, click Restore, and confirm when prompted
- Verify recovery: Check the repository’s contents, test dependencies, and make sure workflows and integrations function correctly
Method 2: Restore GitHub repositories using BackupLABS
GitHub’s built-in recycle bin is handy, but it doesn’t really offer the level of protection your critical code truly deserves. The solution? BackupLABS – a cloud-based backup service that connects directly to GitHub and offers robust data protection.
This paid service offers the following:
- Automatic daily backups (multiple times per day)
- Encrypted storage during transfer and at rest
- Optionally save backups to Google Drive and Dropbox
- Backup and protect repositories, including issues, milestones, commits, branches, labels, comments, Gists, and more
- Detailed audit log
- Easy restoration to GitHub or local device
- ISO 27001/9001 and SOC2 compliance
How to restore a GitHub repository using BackupLABS
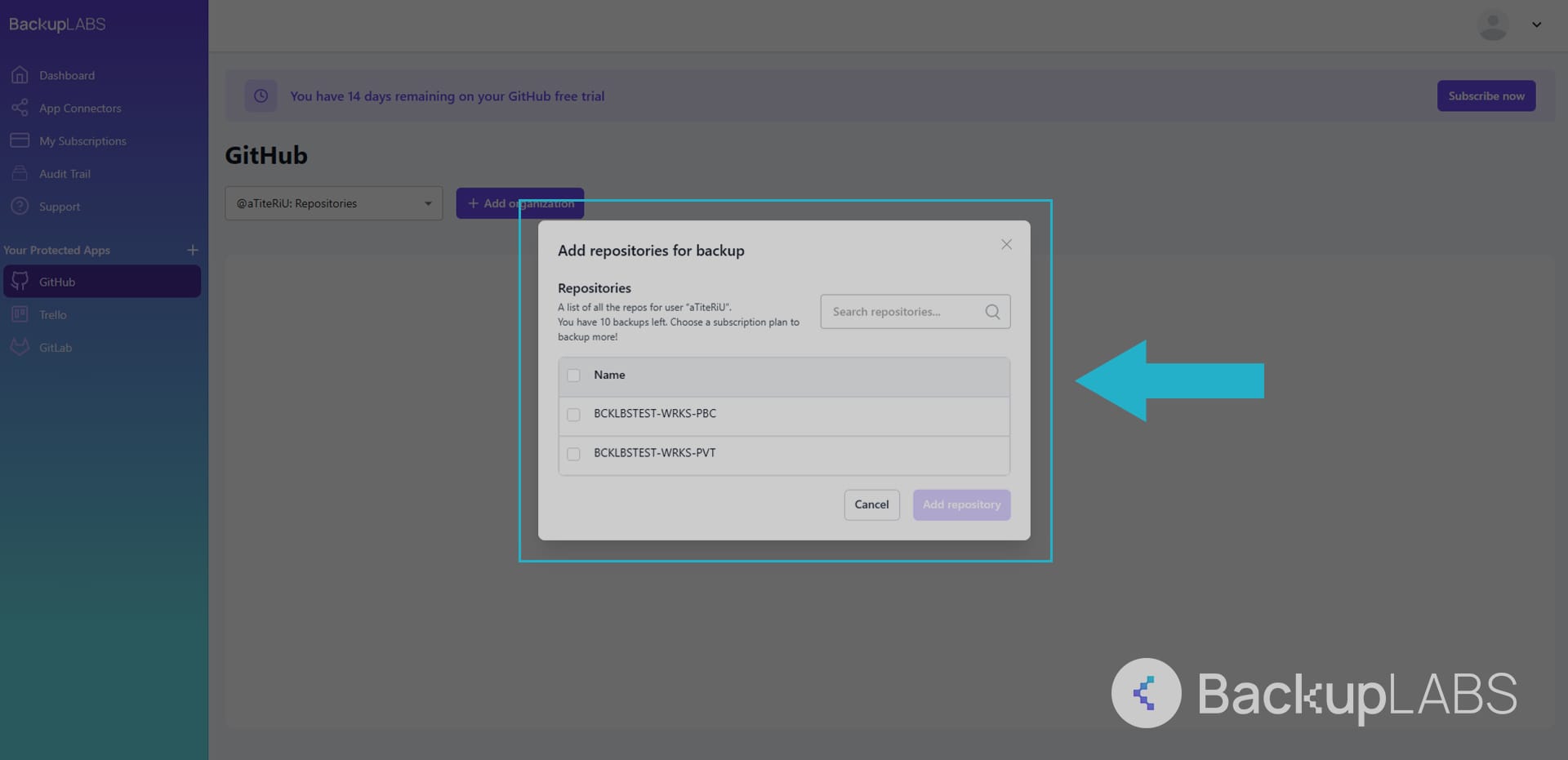
If you’re already a BackupLABS customer and have backed up your GitHub data, here’s how to restore it:
- Log in: Sign into your BackupLABS here: https://app.backuplabs.io/auth/login
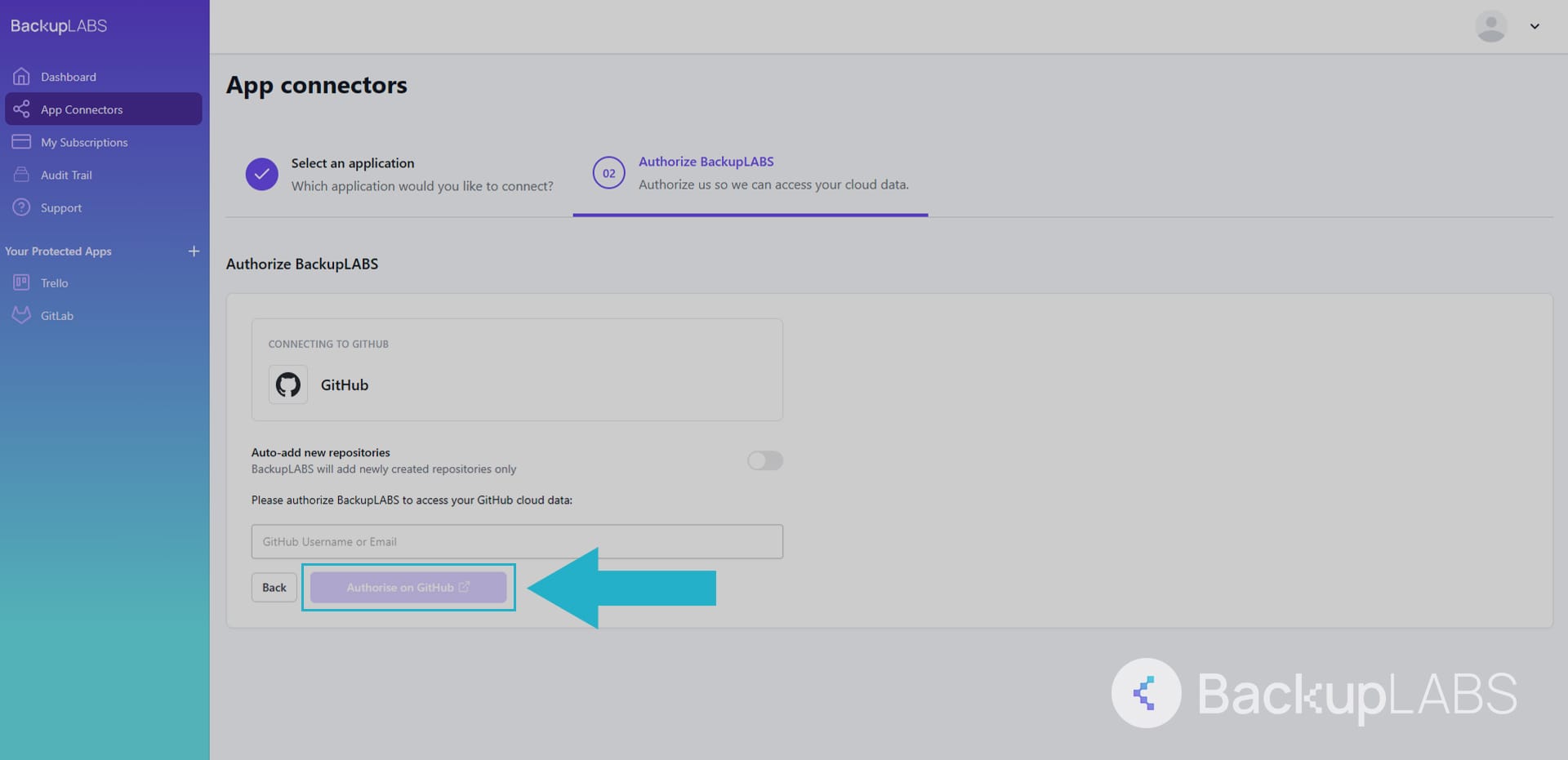
- Select GitHub: On the left sidebar, under Protected Apps, select GitHub
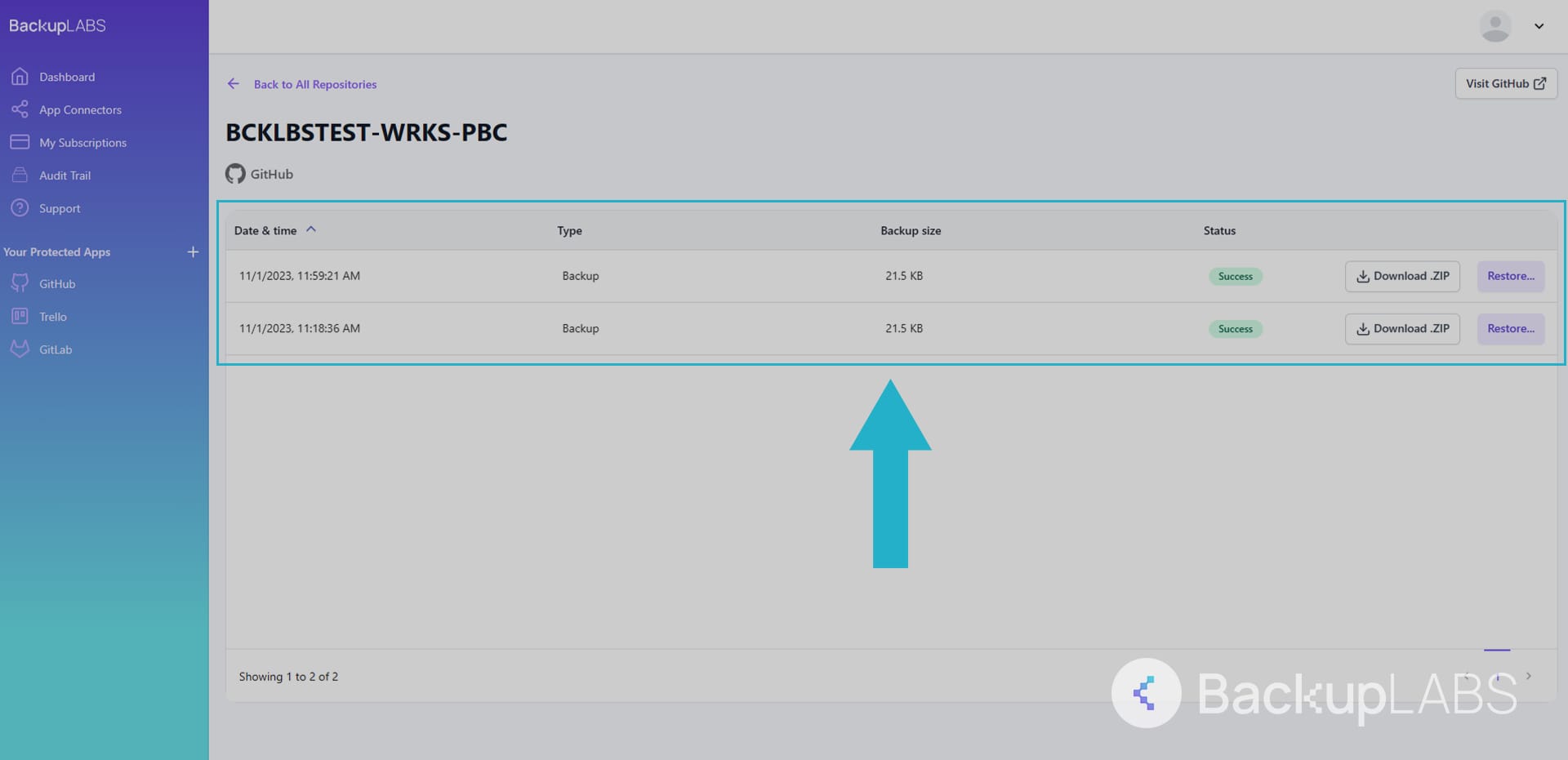
- Locate the repository: Hover over the repository you want to restore and click View
- Select version: Choose the repository version or date you want to restore, then click Restore
- Complete restoration: Review the details, click Confirm, then select Restore
- Access your restored repository: Your entire repository will appear in your GitHub account within a few seconds and will be renamed with “restored_” at the beginning to avoid confusion
What if your repository cannot be restored?
If your deleted repository doesn’t appear in the GitHub recycle bin, the 90-day grace period has passed, or you’re not a BackupLABs customer, recovery options are limited. But there are still a couple of tricks you can try:
- Check local clones: If you or a collaborator cloned the repository to a local machine, there’s a chance its data was pushed to a new repository.
- GitHub Support requests: If your repo isn’t in the recycle bin but the 90-day retention period hasn’t passed, GitHub Support may still be able to help recover it. Be ready to provide details like the repository’s name, URL, and deletion date.
It’s important to remember that GitHub operates under The Shared Responsibility Model. This means that GitHub keeps its platform secure and functional, but it’s ultimately up to you—and only you—to protect and back up your repositories.
Key takeaway
Deleting a GitHub repository can be a nightmare—but it doesn’t have to stay that way. If you act quickly and follow the steps outlined above, there’s a good chance you can get your vital data back or, at the very least, stop a similar incident from ever happening again.
Using a third-party backup solution like BackupLABS is the safest way to automatically protect your repositories. BackupLABS is compliant with SOC2, ISO 27001, and other industry standards to ensure your data is handled with the highest level of security.
Start your free trial with BackupLABS today and keep your repositories safe, secure, and easily recoverable.
GitHub Gists vs Full Repositories: Which Should You Use?Looking to manage your code online? GitHub is a great choice! It offers two main tools for storing and sharing code: Gists and repositories. While these two GitHub features are similar, they serve different purposes.
Today, we’ll break down their differences and clear up the confusion about when to choose a GitHub Gist vs when to opt for a full repository.
What are Gists?
Gists are simple, lightweight repositories designed for sharing single files or code snippets quickly. They’re more streamlined and not as feature-rich as full Git repositories.
Pros of Gists
- Easy to share: Gists let you quickly share small code snippets, notes, or configuration files with a simple link.
- No setup needed: Unlike full repositories, Gists don’t need any setup—just paste your content, save, and share.
- Markdown support: You can use Markdown to format notes, documentation, or to-do lists for better readability.
- Public or private options: Gists can be public for everyone to see or private with a secret link for limited access.
- Track changes: Gists store a full history of edits, letting you view previous versions anytime.
Cons of Gists
- Limited features: Gists don’t have advanced repository tools like branching, issue tracking, or pull request comments.
- Lack of multi-file support: Gists are meant for small code snippets and single files. They don’t work well for complex, multi-file projects.
- Not great for teams: Gists are best for quick sharing, not for structured or large-scale team collaboration.
What are GitHub repositories?
Repositories are the heart of GitHub. With powerful tools for collaboration and version control, they help you manage full-scale projects with ease.
Pros of repositories
- Feature rich: Repositories come with essential tools like branching, pull requests, and issue tracking to keep your projects on track.
- Perfect for large projects: With the ability to handle multiple files and directories, repositories are ideal for dealing with complex codebases.
- Designed for teamwork: Built-in tools—like deployment keys, code reviews, discussions, and automated testing—make repositories ideal for collaboration.
- Connects with other tools: Repositories easily integrate with CI/CD pipelines, GitHub Actions, and more.
- Better presence: Public repositories let you share projects and build your reputation in the developer community.
Cons of repositories:
- Setup time: Getting a repository up and running takes a lot more time and effort than simpler tools.
- Not ideal for small snippets: If you’re only sharing a single file or making a quick fix, a full repository might be overkill.
- Difficult for beginners: Advanced features—like branching and pull requests—are often confusing for new GitHub users.
Key differences: Gists vs repositories
Here’s a quick overview of Gists and repositories.
| Feature | Gists | GitHub repositories |
| Purpose | Fast and easy sharing of code snippets | Full-fledged project management |
| Structure | Single file support | Multiple file support (in folders) |
| Features | Basic version control | Advanced version control (with commit history) |
| Collaboration | Simple sharing features | Advanced team collaboration tools |
| Integration | Limited integration (text editors and IDEs) | Extensive integration (CI/CD, GitHub Actions, and more) |
| Visibility | Public or secret links | Public or private repositories |
When should I use a Gist?
Here are a few circumstances when you should opt for a Gist rather than a full repository:
- Sharing small code snippets: When you only need to share a single file or script, rather than a whole repository.
- Collaborative debugging: When sharing error logs or test cases with others (to troubleshoot and solve problems as a team).
- Embedding code: When embedding GitHub code into websites or blogs directly from the platform.
- Storing notes or documentation: When you need to organise quick notes, guides, or instructions, especially when using Markdown for formatting.
When should I use full GitHub repositories?
Gists are great for quick sharing, but they don’t replace full GitHub repositories. There are still situations where a full repository is needed, including:
- Managing a large project: When your project has many files and dependencies that need to be organised and tracked.
- Collaborating with others: When you need tools like pull requests, issue tracking, and code reviews to collaborate as a team.
- Long-term or complex projects: When you’re working on a project that needs features like structured workflows, version control, and ongoing development.
- Moving large files: When using the REST API, as each file in a Gist can only be 1 megabyte, maximum—which might not be enough for larger files.
Are Gists and repositories backed up by GitHub?
No, neither Gists or repositories are automatically backed up by GitHub. This means if you accidentally delete a Gist or repository or lose access, GitHub doesn’t offer a recovery option.
So what do you do? To ensure disaster recovery and avoid GitHub downtime, we recommend backing Gists and repositories yourself. You can do this by creating your own backup scripts or using third-party backup options.
GitHub backup services like BackupLABS can protect all your repositories and Gists, keeping your data safe and allowing easy restoration if anything goes wrong.
Why protect your Gists and repositories with BackupLABS?
Here’s why BackupLABS is a great choice for backing up your Gists and repositories:
- Automated backups: Our backup policy lets you choose the specific Gists or repositories you want to protect, with automatic backups happening every 24 hours.
- Easy data restoration: No need for any service downtime. Quickly restore your Gist or repository data back to your GitHub account, including granular recovery that lets you roll back to any previous versions when needed.
- Full backup visibility: Keep an eye on your GitHub data backups in real time and catch any errors through your easy-to-use dashboard.
- Data encryption: Rest assured, your Gists and repository data are protected with advanced security measures. They’re encrypted during transfer and while stored, protecting them from security vulnerabilities.
Start your 14-day free BackupLABS trial today.
How to Delete a GitHub Repository in 2024GitHub is arguably the most popular tool for code collaboration. Its cloud-based platform allows developers to work together, share and store code in one central location. GitHub is based on Git, an open source version control system and allows developers to track changes to code over time.
In addition you can also use GitHub for bug tracking, task management and wikis for your projects.
In this guide, we will show you how to delete a GitHub repository and various other important points to consider along the way.
Before you delete a GitHub Repository
You can delete any GitHub repository, commonly known as a “repo” if you have administrator permissions for the repository or are the owner.
Warning! Deleting a repository is a permanent action on GitHub. Once deleted from GitHub it is not possible for GitHub to recover your data. The only way to recover deleted repositories is to use a third party GitHub backup solution such as BackupLABS.
If you delete a public repository, it will not delete any forks. However, if you delete a private repository, all forks will be deleted.
There are a number of things to consider before deleting a repository:
- Archive: You can easily archive a repository. This will allow you to read and also fork the repository but you are unable to make any changes. If your reason for archiving is to free up disk space though, you are out of luck. Archiving does not free up space on GitHub.
- Forking a repository: Forking allows you to create a copy of an existing repository. This fork shares code with the existing upstream repository, but is separate.
- Cloning a repository: Cloning in GitHub repository will create a local copy on your computer. Any changes you do on the cloned repository will sync back to GitHub.
- Backing up a repository: Using a third party backup provider such as BackupLABS will enable you to take automatic daily backups of repositories. If you accidentally delete a repository, you can restore back to GitHub in minutes.
How to Delete a GitHub Repository
Deleting GitHub repositories takes a few minutes to do. Let’s begin.
1. Log into your GitHub account and navigate to the repository you wish to delete
2. Click on Settings:
3. On the General area, scroll down to the bottom until you see Danger Zone.
4. Click Delete this repository:
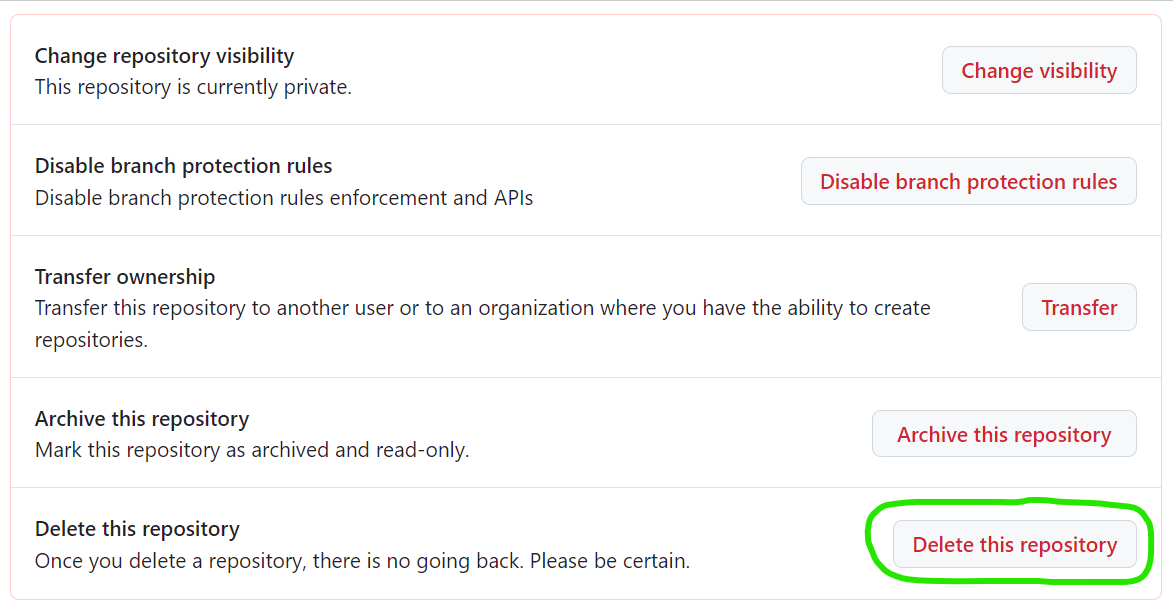
5. Click I want to delete this repository
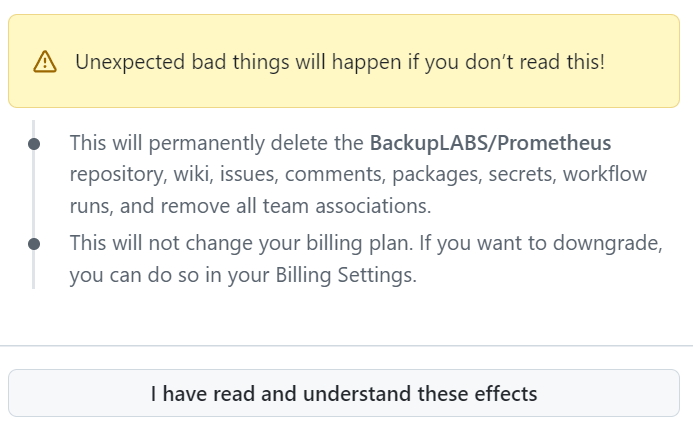
6. You will receive one final warning in a yellow box. Click I have read and understand these effects:
7. Lastly you will be asked to confirm deletion by typing in the name of the account and repository. Then click Delete this repository:
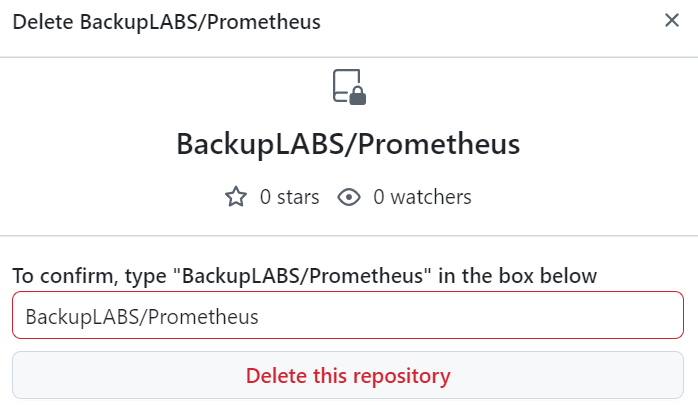
Thats it, your repository has now been permanently deleted.
Summary
Whilst deleting a repository is permanent on the GitHub platform itself, it is possible to still recover deleted repositories by using a third party GitHub backup service such as BackupLABS. A backup of a repository on BackupLABS enables users to restore deleted repositories back into GitHub in minutes.
Based on our research, the most common reason for data loss in GitHub is accidental deletion. Put simply, users are humans, and humans make mistakes. Other increasingly common reasons to recover data from GitHub are nefarious users/employees, bad software updates and viruses/malware. There have also been situations in the past where GitHub have been hacked themselves.
Protect your critical GitHub data today with a free trial of BackupLABS.
Where Does GitHub Store My Data?GitHub is a popular platform for code hosting and version control, the ideal hub where developers can host and collaborate on software projects.
Operating on a large scale, GitHub offers essential tools and services for projects of all types and sizes.
But as we look at the endless projects and functionalities on GitHub, a crucial question comes up: Where exactly is all this data stored?
This blog will explore GitHub’s data storage infrastructure, including its current storage approach – Spokes – and the improvements it’s made to handle the platform’s expanding needs over time.
How GitHub handles data
GitHub repositories are at the core of how the platform handles data, acting as folders or directories for your project files in languages like Python and JavaScript, Ruby, Java, and many more.
When you visit a GitHub repository, the platform does everything in its power to guarantee a smooth loading experience.
The system uses various servers and tools to make sure the repository page you’ve selected loads fast. GitHub uses servers that are spread out around the world to reduce delays and guarantee a smooth experience, no matter your location.
Initially, GitHub relied on Rackspace to store data due to its speed and dependability. But as the platform’s user community expanded, GitHub shifted to Spokes, its own infrastructure designed to effectively handle the increased storage demands.
Improvements in GitHub’s storage over time
Spokes marked a significant milestone in GitHub’s evolution. It provided a foundation for better performance, scalability, and reliability.
Switching to its own storage infrastructure means GitHub can better manage its growing volume of user traffic and data. With this new approach, Github can add more servers as needed without compromising on performance or user experience.
These advancements show Github’s dedication to guaranteeing it remains a top platform for hosting code and facilitating collaboration for many years.
Spokes: GitHub’s advanced storage system
Spokes is different from other storage methods because it uses a distributed approach. This means it can replicate and store data in multiple locations around the world for added security.
Here’s how Spokes benefits you:
- Enhanced data security: Replication protects your code from hardware failures, network issues, or disruptions at a single site. By guaranteeing data remains accessible from different locations, Spokes minimises downtime and maintains data integrity.
- Improved accessibility and performance: Spokes’ distributed storage system optimises data retrieval to improve efficiency, minimise delays, and boost overall performance. Regardless of location, you can trust that your code is safely stored and easily accessible.
The limitations of GitHub storage
Despite its updated storage infrastructure, Github’s ability to protect your data is still limited. The platform operates under The Shared Responsibility Model, which means you also play a crucial role in managing and protecting your data.
Potential scenarios where Spokes could lead to data loss include network outages, data consistency issues, hardware failures, and cyberattacks.
Under the Shared Responsibility Model, you can complement GitHub’s storage infrastructure with additional backup and recovery solutions from third-party vendors.
Importance of third-party backup services
Losing critical data can have serious consequences for your company. It can lead to downtime, financial setbacks, and reputational damage.
It’s important to have a third-party Github backup solution like BackupLABS in place to reduce these risks and maintain seamless business operations.
The benefits of third-party backups include
1. Data protection
Your data is vulnerable to hardware failures, cyberattacks, human errors, natural disasters, and other threats. Third-party backup solutions safeguard your critical information by providing an additional layer of security and enabling quick restoration of lost or corrupted data.
2. Legal protection
The extra security offered by third-party backup solutions is particularly beneficial in regions where strict guidelines govern data storage locations.
These laws, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Data Protection Act, specify criteria for handling and storing the personal data of individuals living in the UK.
You can obey the law by choosing third-party backup services that meet regulations while protecting your valuable information.
3. Business continuity
Using external backup systems reduce downtime, helping you maintain business operations during data loss or disruptions.
Restoring data quickly allows critical business functions to restart promptly, minimising financial risks and preserving customer confidence.
4. Scalability
Many third-party backup services offer scalable solutions for your business’s growing needs. Whether a small startup or a large enterprise, these services can adapt to your changing data storage requirements without compromising performance or security.
Why use BackupLABS as your backup solution?
With BackupLABS, you can enjoy a reliable and feature-rich backup solution, excellent customer support, and robust security.
BackupLABS offers a comprehensive backup solution with the following features:
- On-demand account backups: Securely back up all your data whenever you need, without any restrictions. Plus, easily create pull requests to propose changes to your backed-up data.
- Automated revision tracking: Easily access previous versions of your repositories and track changes effortlessly.
- Manual download: Download your archive files privately in zip format for offline access or sharing.
- Bulk restoration: Restore multiple files at once, simplifying the recovery process.
- Instant cloning: Use backups to create clones of your data instantly, as many times as required.
- Comprehensive metadata retention: Ensure that your repositories retain all necessary data for future reference.
- Dedicated customer support: Access dedicated customer support whenever you need assistance.
- File renaming support: Optionally rename restored files for easy identification and organisation.
- Security alerts: Receive alerts and notifications to stay informed about security-related matters.
- Website security and encryption: BackupLABS ensures website privacy, security, and compliance with industry standards like SOC2 and ISO accreditation.
Does BackupLABS cloud storage solution sound like the right choice for your organisation? Sign up for our 14-day free trial to try it for yourself.
Expert Insights: How to Recover Deleted Files in GitHubIf you’ve accidentally deleted a file or repository in GitHub, you’re not alone. It’s a relatively common occurrence — but it’s one that can cause significant disruptions to your development workflow. From a misplaced keystroke to an oversight during a code cleanup, file deletion can create unnecessary stress for your teams, and in some cases, derail entire projects.
And, while several methods for recovering deleted GitHub files do exist — not all are equal.
To help, we’re here to talk you through the different ways to recover GitHub data, and get your projects back on track as soon as possible!
Recovering deleted GitHub files
If you work with GitHub, you’ll already know that recovering data isn’t just a matter of pressing a “recover all” button.
Due to the complex nature of GitHub data, the steps will differ for every recovery scenario to ensure your data is recovered correctly and the integrity of your project is preserved.
When trying to recover deleted files, there are two common approaches users can take:
Command line methods
For those comfortable with the command line interface, Git commands can recover deleted files at different stages of deletion. For example, if you’ve accidentally deleted a file but haven’t staged the changes yet, you can use ‘git restore’ to bring it back instantly.
But, if you run this command after the changes have been staged, you’ll likely come up against an error code. This is because the file no longer exists in that index.
In this case, commands like ‘git checkout’ and ‘git show’ can help you locate the commit where the file was deleted and restore it from there. But, technical proficiency is advised.
In short, while a command line method can offer immediate results for file recovery, its success will depend on your level of technical knowledge and the speed at which you work.
GitHub desktop and Web UI
If you prefer a more visual approach, GitHub’s Desktop app and Web UI provide graphical methods for recovering deleted files.
For example, in the GitHub Desktop app, any changes you make in your repository will show up in the staging area in the left sidebar of the app. From here, you can revert changes to a previous commit that includes the deleted file. But, this only applies if you have not yet committed the deletion, and also relies on platform availability (which is currently limited).
If you have committed the deletion, the GitHub Web UI allows you to browse through your commit history and download the deleted file directly from the browser. But, because there’s no way to select and download more than one file, you have to download them one by one — a slow and arduous process.
While these methods may be more accessible for users who prefer a less technical approach, they’re not known for handling multiple files or complex recovery scenarios efficiently.
Restoring deleted GitHub repositories
GitHub’s restoration feature
GitHub offers a built-in restoration feature that allows personal account users and organisations to restore deleted repositories within 90 days of deletion.
To restore a deleted GitHub repository, navigate to your GitHub settings and select the repository you wish to restore. From there, you can confirm the restoration action, and GitHub will restore the repository to its original state.
While this feature is useful in certain cases, it’s important to note two things; first, that a user can’t restore repositories in a fork network. And second, that restoring from different commits can create inconsistencies in your data. Sometimes, it’s not worth the risk.
Tip: Whether you’re working with a parent repository, local repo, or other repository, make sure other team members are aware of any changes or restoration actions to maintain consistency across your project. When creating a new repository, it’s also important for team members to have more than basic knowledge of local repository management. From a simple commit hash to how a repository’s forks work, the wrong information can lead to data inconsistencies and project setbacks.
The role of third-party backups
When it comes to GitHub recovery — or any data recovery for that matter — it’s always wise to have a backup plan in place.
This is where a third-party GitHub backup solution like BackupLABS comes into play.
Third-party backup solutions offer an extra layer of protection against accidental deletions, system failures, or other unforeseen events.
Here’s what you need to know:
Enhanced security and convenience
While GitHub provides some native features for data recovery, relying solely on these may not always be sufficient. Third-party backup services like BackupLABS offer enhanced security and convenience by continuously backing up your GitHub data.
This ensures that you have a reliable backup solution in place, providing peace of mind and simplifying the recovery process in case of accidental deletions.
Features of BackupLABS
BackupLABS offers a range of features designed to meet the needs of GitHub users. From automated backups to customisable coverage, BackupLABS ensures that your GitHub data is always protected — on your terms!
BackupLABS also provides easy-to-use tools for restoring from backups, allowing you to quickly recover deleted files and repositories from your last backup, in just a few clicks!
Setup and Usage
Getting started with BackupLABS is simple. After syncing up permissions with your GitHub account, you can select which repositories you want to back up.
It also offers the option to back up all repositories automatically, backing up new repositories created on GitHub without any additional effort. With nightly backups and snapshots saved for 30 days, BackupLABS provides a reliable solution for safeguarding your GitHub data.
Schedule a demo of BackupLABS
Don’t let accidental deletions derail your projects. Instead, take a proactive step towards a more seamless way of working by scheduling your demo of BackupLABS or get started with a free trial today.
How To Backup GitHub Repositories & MetadataIf you’re a software engineer or company using GitHub, safeguarding the data stored within GitHub is paramount.
The loss of valuable code repositories, critical project files, customer data, and more can have severe consequences that can impact your business operations.
In this blog, we’ll highlight the importance of prioritising content backup for your GitHub data. We’ll also share a range of manual backup strategies to help you effectively safeguard your data.
By implementing these strategies, you can mitigate the risks associated with data loss and ensure the safety and accessibility of your valuable information.
However, it’s important to recognise the limitations of manual data backup solutions. That’s why we’ll also explore how SaaS app protection solutions, such as BackupLABS, provide an effective and reliable alternative.
The importance of backing up your data from SaaS Apps such as GitHub
Here are the main reasons backing up your cloud data is a must:
- Legal Obligation: Data protection laws, such as GDPR, require regular backups to protect personal online data and ensure its security and integrity. While SOC 2 and ISO standards are not specifically mandated by law, many companies recognise their importance and choose to implement them to enhance data security and compliance
- Ransomware: Regular backups provide an additional layer of defence against ransomware, minimising the impact of attacks and facilitating data recovery
- Safeguarding against humans: Backing up your content from online apps helps mitigate the consequences of accidental deletion, file overwriting, malicious humans (eg disgruntled employees), or unintended modifications, allowing you to restore previous versions or retrieve deleted files
- Downtime: Proper backups ensure that critical data is readily available for recovery in the event of server failures, system crashes, or cybersecurity incidents, minimising downtime and reducing the impact on business operations
The limitations of backing up your data manually
While manual solutions like downloading the zip of your repository offer some level of data protection, it’s crucial to weigh the associated limitations, potential risks, and the impact on employee productivity.
- Employee cost and time: Manually downloading the repository zip requires dedicating employee time and resources. Depending on the size and complexity of the data, this process can be time-consuming, diverting valuable resources away from other important tasks
- Prone to human error: Manual data protection methods are more susceptible to human error. Mistakes such as incomplete or incorrect backups can occur during the manual downloading process, potentially compromising the integrity of your data
- Limited revision history: When downloading the repository zip file, it’s only going to capture the data at that moment. This means that previous revisions, comment history, and changes made over time may not be preserved. Retaining a comprehensive revision history can be crucial for tracking progress, identifying issues, and reverting changes if necessary
- Incomplete metadata: Manual downloading may not guarantee the preservation of all the metadata associated. This can include important information such as file properties, timestamps, authorship, and other contextual details. Maintaining metadata can be essential for proper data management, compliance, and future analysis
Automated backups like BackupLABS provide a more reliable and efficient way to preserve your data, ensuring comprehensive metadata, revision history, and ease of data restoration when needed.
How to back up your GitHub repositories
There are several methods you can use to protect your data stored on online apps.
Here are a few options:
Method 1: GitHub – Manually downloading your repository zip
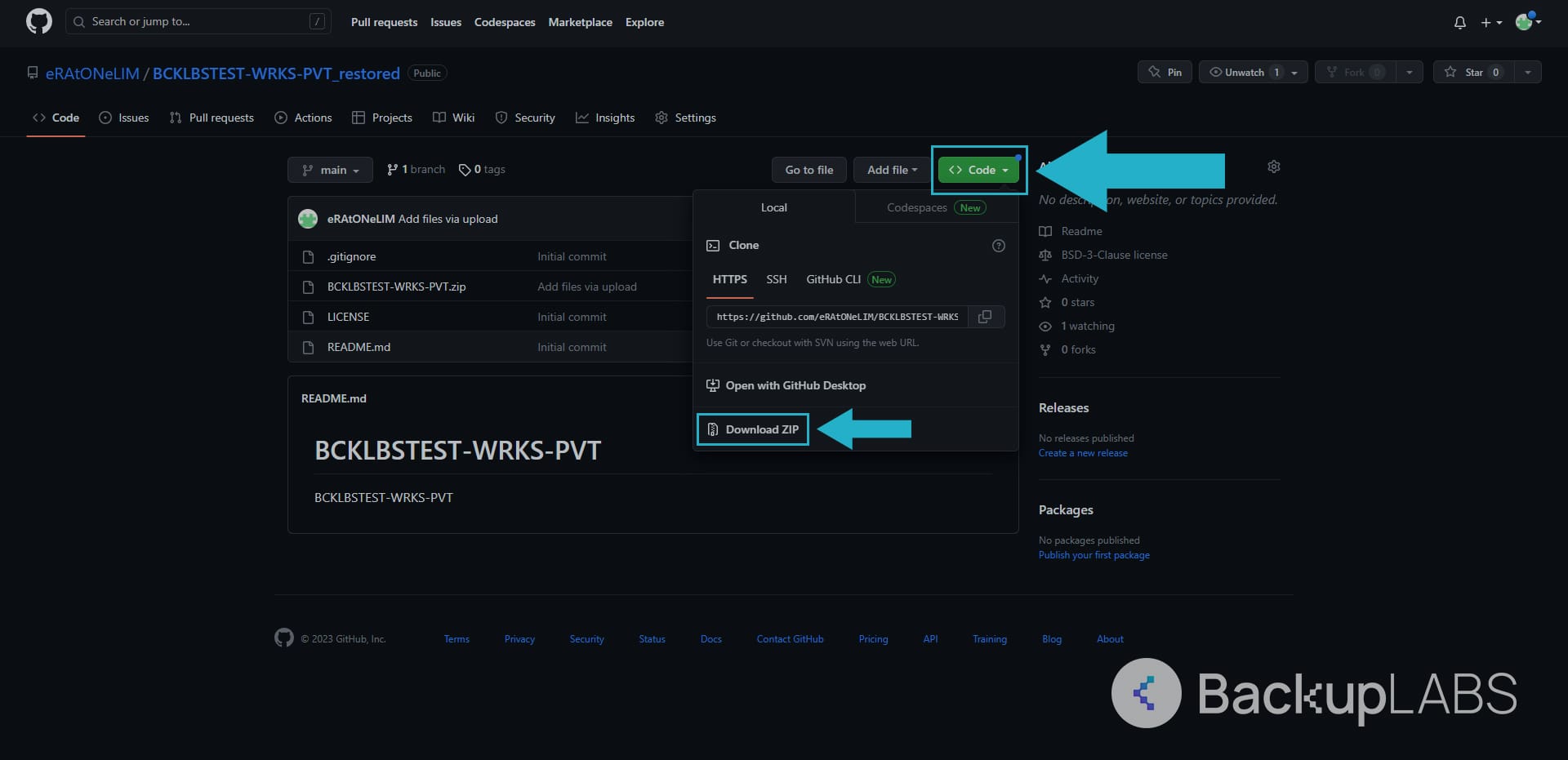
The “download zip” option allows you to download the repository as a compressed zip file containing all the files and folders in the current state.
Downloading Repository Zip
- Go to the repository. Under the Code tab at the top, use the Code drop down and at the bottom, select Download Zip

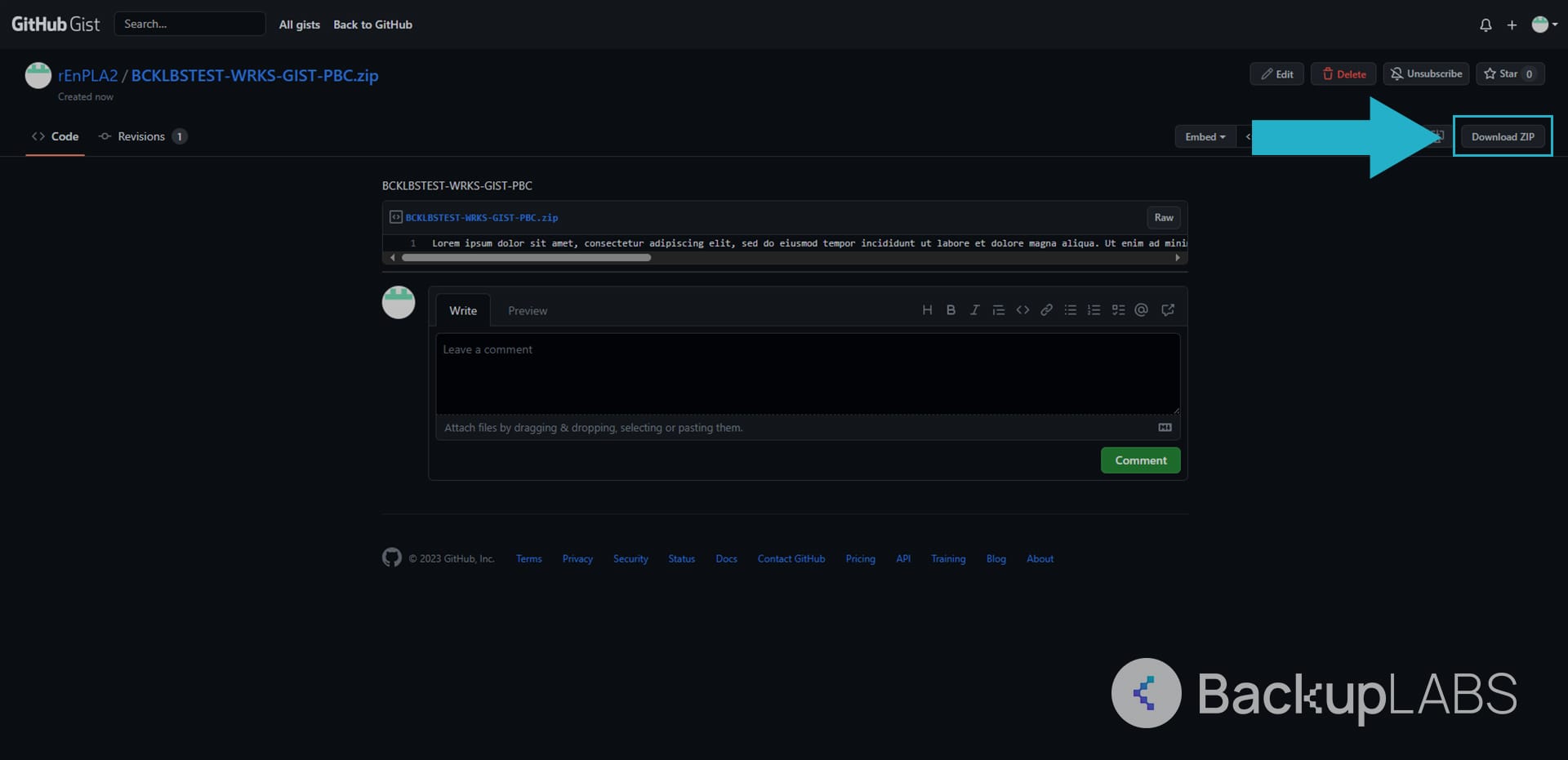
Downloading Gist Zip
- On your Gist, select Download ZIP in the top right of the page

Pros:
- Snapshot of current state: The downloaded zip file provides a snapshot of the repository’s current version, capturing all files and folders
- Offline access: Once downloaded, the zip file allows for offline access to the repository’s content
Cons:
- Limited version control: The zip file doesn’t retain the revision history of the repository, making it difficult to access previous versions or track changes over time
- Incomplete metadata: Comprehensive metadata associated with the repository, such as commit messages and timestamps, may not be preserved in the zip file
- Manual backup management: The responsibility of regularly downloading and storing updated zip files rests on the user, which can be prone to human error or oversight.
Method 2: Git Bash – Manually cloning a repository
- Open the repository on GitHub
- Click on the <> Code button at the top right of the repository page
- In the Clone section, copy the provided URL (HTTPS, SSH, or GitHub CLI) based on your preference
- Open Git Bash on your local computer
- Use the cd command to navigate to the desired location where you want to clone the repository. For example:
cd Documents/Projects/ - Execute the git clone command followed by the copied URL to start the cloning process:
$ git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/YOUR-REPOSITORY - During the process, you will see progress updates, such as counting objects, compressing objects, and unpacking objects:
> $ git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/YOUR-REPOSITORY > Cloning into `Spoon-Knife`... > remote: Counting objects: 10, done. > remote: Compressing objects: 100% (8/8), done. > remove: Total 10 (delta 1), reused 10 (delta 1) > Unpacking objects: 100% (10/10), done. - Wait for the cloning process to complete
Pros:
- Offline access: Once cloned, you can work with the repository offline, without the need for an internet connection
- Version control: Cloning preserves the entire revision history of the repository, enabling you to track changes and access previous versions of files
Cons:
- Limited backup functionality: Primarily focuses on creating a local copy of the code and does not provide comprehensive backup features
- Lack of metadata preservation: While cloning captures the content of the repository, it may not preserve all the metadata associated with it
- Manual update process: Requires manual actions to keep the local copy up to date with the latest changes in the repository, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors
- Single point of failure: Provides a single local copy, making it susceptible to data loss in case of hardware failures, accidents, or other unforeseen events
- Coding You will need coding literacy to understand and run the commands necessary
Method 3: Git Bundle – Manually cloning a repository
To use Git Bundle, create a bundle file, verify its content, and add it as the origin for a new repository. Here are the Git Bundle commands you can use:
- Create a Git Bundle:
git bundle create [-q | --quiet | --progress] [--version=] <file> <git-rev-list-args> - Verify a bundle:
git bundle verify [-q | --quiet] <file> - List the heads in a Git Bundle:
git bundle list-heads <file> [<refname>…] - Unbundle a Git Bundle:
git bundle unbundle [--progress] <file> [<refname>…]
Pros:
- Offline transfer: Allows offline transfer of repository branches as .pack files, enabling you to work with repositories without an internet connection
- Version control: Preserves the full history and revision information of the repository
- Open source: A popular open source solution made by GitHub members
Cons:
- Manual labor and monitoring: Requires manual effort and monitoring, leading to increased time consumption and potential human errors
- Limited comprehensive backup: Lacks automated scheduling, redundancy, and additional backup features found in dedicated backup solutions
- Potential for accidental modifications: Using Git Bundle manually may result in unintentional modifications to the repository due to the need for manual actions and management
- Complexity and limited support: Can be complex to work with, and support may be limited as it relies on the open-source community for assistance and updates
Method 4: BackupLABS – Automated GitHub backups
BackupLABS provides an effortless and automated solution for backing up your valuable GitHub repositories.
In just four simple steps, you can securely back up your data and enjoy easy access to your repositories at any time. Here’s how it works:
- Create a BackupLABS account

- Connect your GitHub account

- Choose what you want to backup

- Access your repositories and their revision history at any time

Why use BackupLABS as your backup solution?
With BackupLABS, you can enjoy a reliable and feature-rich backup solution while benefiting from excellent customer support and robust security.
BackupLABS offers a comprehensive backup solution with the following features:
- On-demand account level backups: Backup all your data anytime, without limitations
- Automated revision history: Retain and access iterations of your repositories
- Manual downloads: Privately download the zip files for your archive
- Account level restoration: Restore multiple files in bulk
- Create clones instantly: Use backups to create as many clones as you like
- Comprehensive metadata: Know your repositories retain as much data as possible
- Customer support: Dedicated customer support is available to assist you
- File renaming support: Optionally rename your restores with new names to easily identify
- Security alerts and notifications: Stay informed with security alerts and notifications
- Website security and encryption: BackupLABS ensures website privacy, security, and compliance with standards like SOC2 and ISO accreditation
Try BackupLABS for yourself, sign up for our 14-day free trial.
How do I backup GitHub & why do I need to?You’ve just launched a brand-new application, utilizing GitHub as your Git repository. All your hard work, planning, time, and effort has finally paid off. The first month has been incredible, and you have gained many new customers. Everything is going as planned…
Then, one Monday morning, a member of your team informs you that your GitHub data has been deleted somehow. Completely disappeared.
In all the excitement of launching your revolutionary new app, you didn’t back up your critical development assets. Now, the code that you have spent thousands of hours (and money) working on has gone.
But surely GitHub itself is a backup, so backs up my data automatically?
Kind of… GitHub stores the most recent code and files, not all the versions and edits that have gone before it. It’s a bit like an autosave feature without the history.
Data loss can happen at any time and there are several potential causes, some of the most common include:
- Human error – Users make mistakes and accidental deletion of repositories is the most common reason for data loss.
- Nefarious users – Disgruntled employees who still have access to your system could wreak havoc and maliciously delete your data.
- Platform issues – No cloud app can guarantee 100% uptime, and we’ve even seen cloud providers accidentally lose user data.
- Outages – In 2017 and again in 2020 there was a major outage of the GitHub service leaving many companies without access to their code and the possibility to work.
- Ransomware and viruses – Unfortunately, this risk is becoming more common and is now seen on cloud apps, including GitHub, not just desktop computers.

Why is it important to back up your GitHub data?
Losing your data could be catastrophic for your business. Think about your company
– how long would you be able to work without access to your GitHub data? What have you got to lose? What would be the financial fallout to your company having no access? Could you afford it? Or are you better to prevent such situations and invest in a reliable third-party backup (with us)?
As GitHub is a cloud based service it also adheres to the Shared Responsiblity Model. In short it means that they look after their server infrastructure, the application and network. The actual data, your data and responsibility of it remains with you.
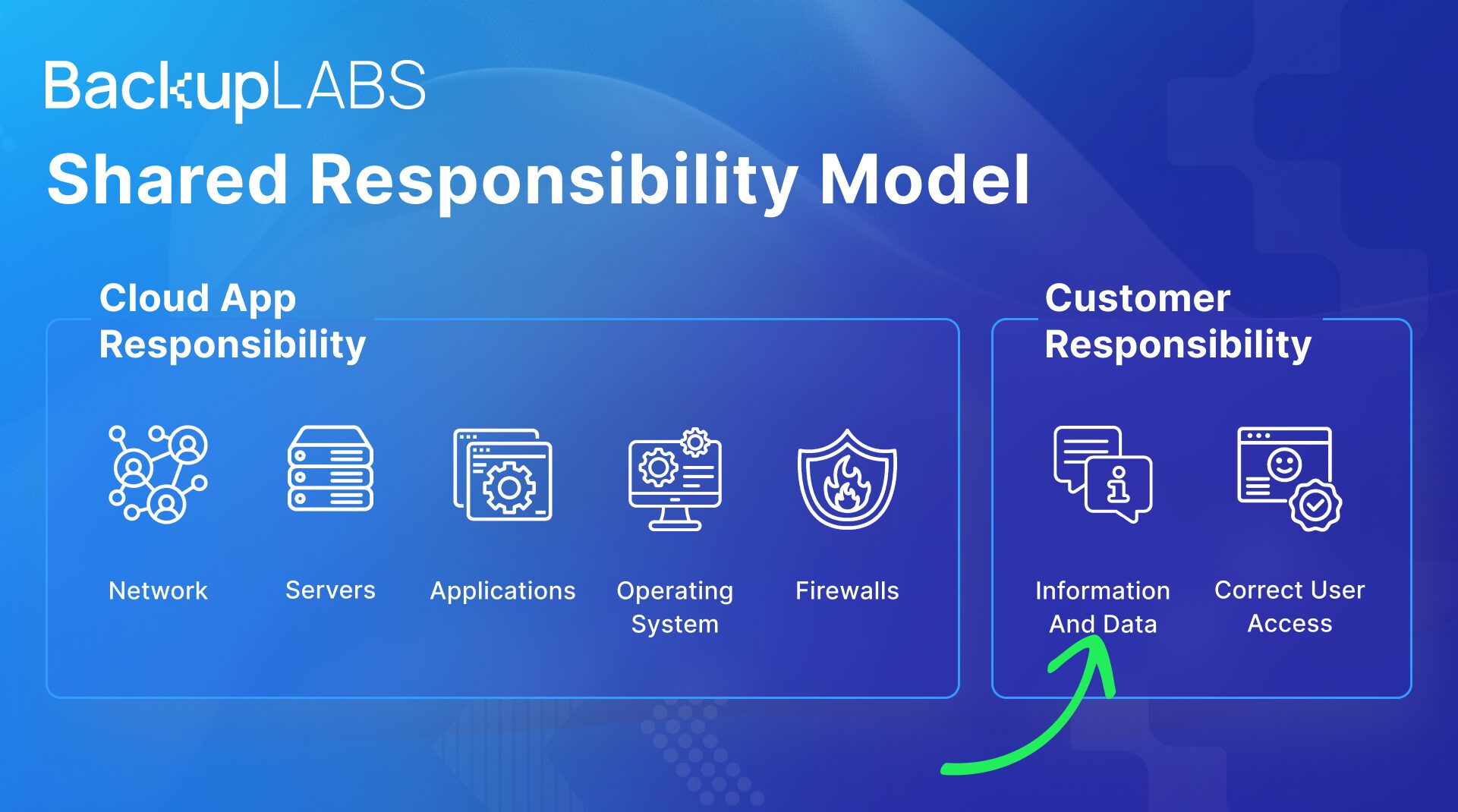
So, how do you backup GitHub?
Essentially, there are two methods for backing up your GitHub repositories. You can do it yourself (in-house) or work with a backup provider (third-party) to do it for you. We often say to our customers, your data is always your responsibility – you need to make sure it’s properly protected – and it is with us!
In-house backup
Taking things in-house gives you complete control in backing up your GitHub repositories. You can decide how the system is managed, how it integrates with other parts of your business, what can be backed up, and how often you can backup.
There are two popular open-source scripts you can install to backup your own data: Python GitHub Backup script and Amazon S3 Backup GitHub Action.
These open-source scripts are easy to implement, and the code is stable, widely used, and free. After installing the scripts, they allow you to choose which repositories you want to back up and specify which resources within those repositories. You can then choose where to send the copy of the data.
However, there are limitations to these free scripts. To back up, you must run them manually, because there is no automatic backup at a regular set time. But one of the biggest concerns is that there is no option to encrypt your backups. This lack of security will potentially leave you open to attackers who could steal and exploit your code. If you are subject to any kind of regulations such as HIPPA or GDPR you may need to show you have a separate backup of your data. Assuming that GitHub has a backup isn’t good enough – they will ask you to prove it.
The other thing you will need to consider when managing your own backups is manpower. Unless you are willing to take on the task of backing up yourself, you will require a dedicated individual or team to complete the backup and manage it. In reality, a backup script is setup once, tested for a week or so, then left. Unfortunately, these types of scripts are barely tested to see if they restore. If you are running a manual GitHub backup script, when was the last time you tested that actually restores successfully?
Third-party backup
If you’d prefer to work with a third-party organisation that will take care of your backup, then look no further than BackupLABS. Our backup-as-a-service platform automatically backs up your GitHub repositories, and metadata (including milestones, projects, pull requests, wiki, releases), to ensure you never lose access to your critical code.
Installing and configuring our solution is easy thanks to GitHub Marketplace integration, and our free trial allows you to try before you buy.
Once installed, we will automatically back up your repositories each day. Backups are encrypted during transfer and at rest and are stored securely on our servers with 256 bit AES encryption, with the option to save them on your own Dropbox or Google Drive account if you wish.
When you need to use your repository backup, you can either restore it directly into GitHub or restore the repository from BackupLABS onto your local machine. This ensures that in the event of an outage, you can access your data whenever you need to. We also provide you with an audit log so you can keep track of your backups for compliance and security purposes. We know that recovery is an essential part of backing up your data, so our solution enables you to recover your repository at any point in the past 30 days, and more if required.
The benefits of backing up GitHub
- Peace of mind. If data is compromised, backups are extremely helpful in providing a previously good state to compare with the current state. If you only have your infected codebase, it can be challenging to uncover all the corrupted files or backdoors left open for future attacks.
- Saves money. Ransomware attacks take control of codebases or sets of infrastructure and demand money in return to unlock the encryption they have added. Having backup of your repository would mean you could restore from your backup and continue working with minimal downtime – not to mention saving your business £££’s as the ransom would not need to be paid, as unlocking the encryption would not be required.
- Saves time. GitHub has a 90-day recovery period for deleted repositories – but there are limitations to this feature. Having a backup and restore plan (with frequent automatic backups in place) with a third party, ensures a minimal negative impact to your business and a quick recovery to your GitHub repositories – it’s the difference between a work-stopping outage causing days out or even having to close your business, to a simple alert and switchover.
- Maintaining compliance. Our backup solution ensures that personal data is compliant with GDPR. If you’re subject to SOC 2 compliance standards, you’ll choose from 5 Trust Services Criteria categories, Security (or Common Criteria), Availability, Confidentiality, Processing Integrity and Privacy. SOC 2 auditors will check that backups of certain database components and applications are performed daily to support recovery in the event of a service failure. The SOC 2 also demonstrates that you take security seriously and have invested in processes and systems that will protect sensitive data and information – it’s a great competitor advantage too.
If you need a reliable and robust backup partner, head our GitHub Backup page to get started. You’ll be up and running within 5 minutes!
Let us take care of your data while you take care of the rest of your business.